Ideje 199+ Atom 3 Subatomic Particles Čerstvé
Ideje 199+ Atom 3 Subatomic Particles Čerstvé. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom.
Prezentováno Subatomic Particles Atoms Are Composed Of Three Particles Protons Neutrons Electrons Particles Can Be Distinguished By Their Charge Mass And Location Ppt Download
These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e.
Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon).
In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of.. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.

Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles.

Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table.

Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated ….. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e.
The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons.. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom).

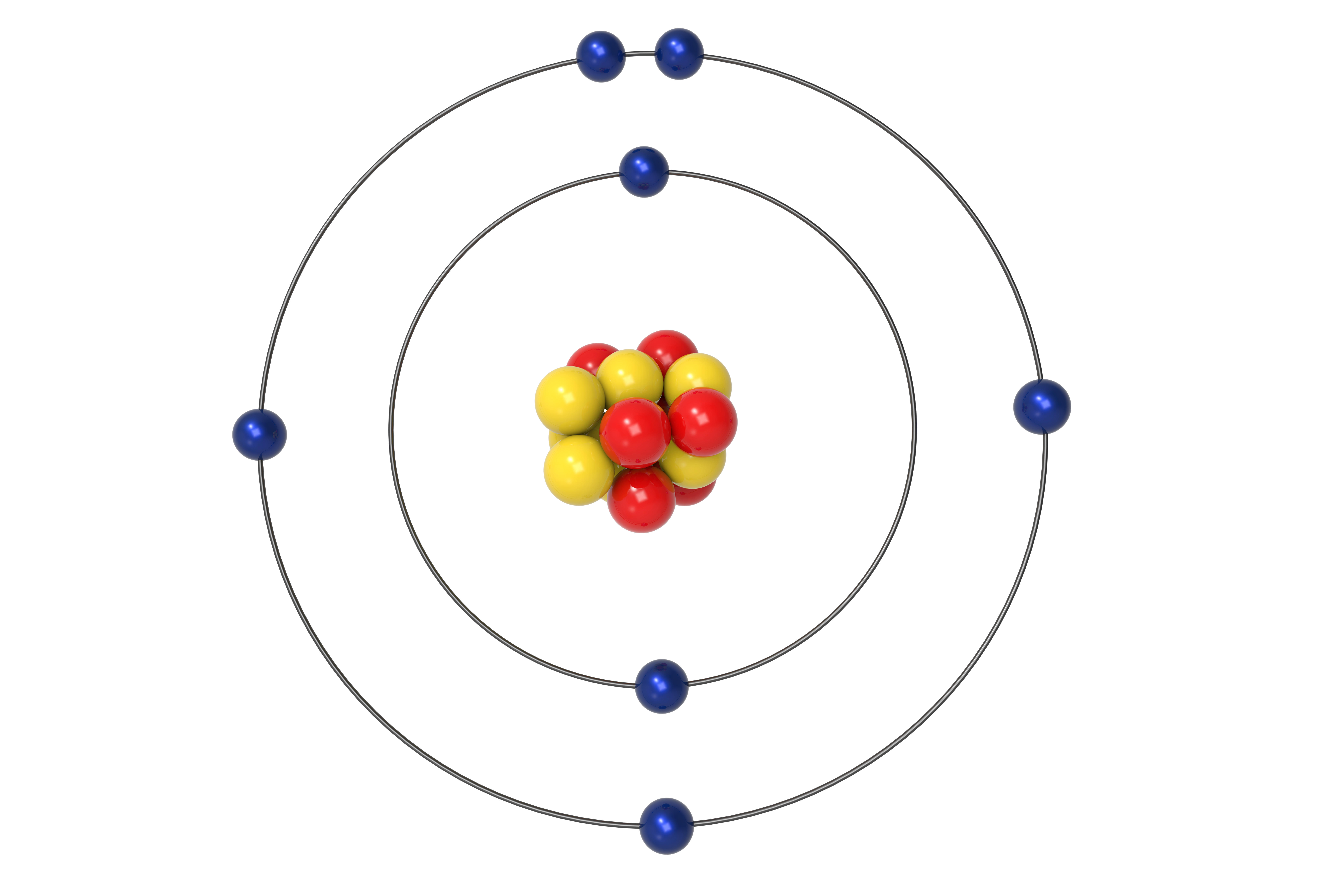
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated …. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom).
These subatomic particles have mass. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g.

The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated …. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles... Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom).

Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral... All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. These subatomic particles have mass. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table.
Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral.. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.

Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table... Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral.

Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons... Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles.

All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons... Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons.

These subatomic particles have mass. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.

These subatomic particles have mass. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g.

Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). These subatomic particles have mass. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles.

A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. These subatomic particles have mass. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used.
Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. . Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles.

In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons.. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom).

Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide.. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e.

In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:.. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. These subatomic particles have mass. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … These subatomic particles have mass.

Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom.
Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except …. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e.

In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom.

Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. .. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide.

In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.

Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral.. These subatomic particles have mass.

Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral... He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.

The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated ….. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral.. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except …

All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons... In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.

May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. These subatomic particles have mass. Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.
Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except …. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … These subatomic particles have mass. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon).

Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. These subatomic particles have mass. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom).
May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. .. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom.
Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. These subatomic particles have mass... Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e.

May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom... These subatomic particles have mass. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles.

Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used.. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.. Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles.

Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles... Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except …

Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of.

Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells... Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon).. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.

Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.

Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … .. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells... In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used.. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom.

Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated …

Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells... Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide.

Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e.. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles.

Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. These subatomic particles have mass. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles.

Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. These subatomic particles have mass. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table.. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:

All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.. Thomson discovered that cathode rays are not electromagnetic waves but made of particles that are 1,800 times lighter than hydrogen (the lightest atom). In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles.

Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand: These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Other subatomic particles may be found in association with these three types of particles. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Sep 20, 2021 · a single subatomic particle can strike an atom of 235 u, splitting it into 2 separate atoms of other elements and releasing 3 neutrons.. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral.

A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. .. In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:
Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral.. These subatomic particles have mass. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.

All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons.. These subatomic particles have mass. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that is smaller than an atom. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table.. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used.

The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated …. Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom's bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom's compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. Three types of subatomic particles are commonly used. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei (except … Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Thomson concluded that these particles came from the atoms within the cathode — they were subatomic particles. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.. He called these new particles corpuscles but they were later renamed electrons.

Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of. May 18, 2018 · subatomic particles subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. Answer each of the following using your knowledge of chemistry and the periodic table. A neutron gun) or can be generated when nuclei collide. All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. These subatomic particles have mass. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated … Identify the neutral atom described by name and mass number (i.e. These particles can come from a moderated source (e.g. According to the standard model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon).. These subatomic particles have mass.
